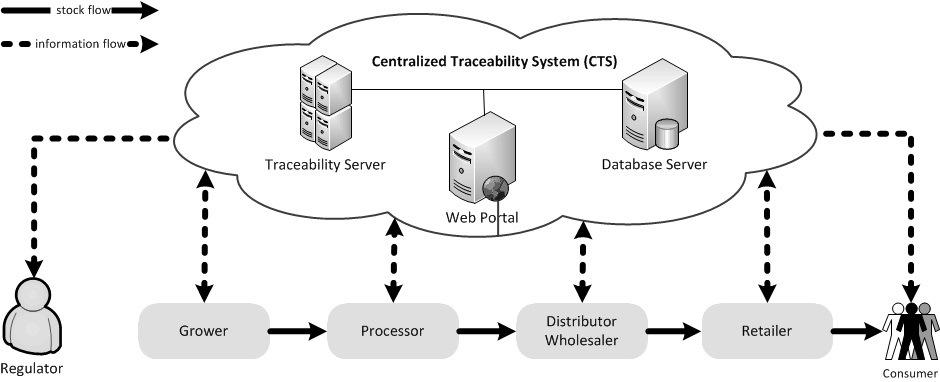
Our centralized traceability system (CTS) consists of three function modules: traceability server, database server and web portal. It creates very few overheads for supply chain partners as the servers are centrally hosted and only a thin application (typically a web browser) with internet access is required on the client side. As shown in the figure, the web portal handles all incoming and outgoing traffic with traceability server encapsulating the entire traceability logic and database server storing the traceability data respectively. CTS is hosted on an elastic cloud platform offering high scalability. Supply chain partners upload traceability data to CTS throughout their entire business process and retrieve traceability data on demand. By pulling information from CTS, consumers can see the full history of the purchased product and regulators can generate a macro picture of the farm to fork traceability as well as drill down details.
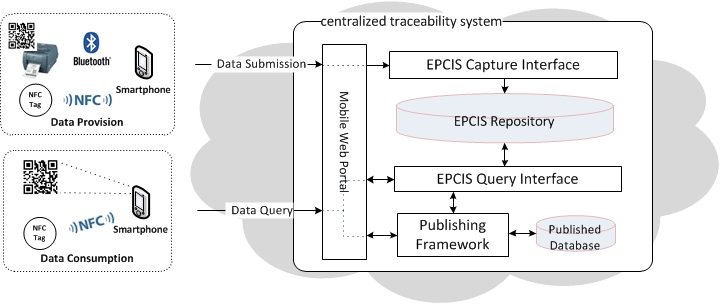
To achieve better compatibility and extendibility, the traceability server is designed on the basis of Electronic Product Code Information Services (EPCIS) which is an EPCglobal standard designed to enable EPC related data sharing within and across enterprises. EPCIS facilitates internal data capturing as well as external sharing of information about the movement and status of goods in the physical world (EPCglobal, 2007). The EPCIS specification version 1.0.1 defines two interfaces and a data model. As illustrated in Fig.3, traceability data is submitted from client through EPCIS capture interface and is stored in EPCIS repository. Similarly, client sends request and retrieve data through EPCIS query interface. Since the traceability data may look industrial and exhausting for consumers, a publishing framework is designed to join/filter/transform the raw data to suit different interest. To obtain a better system performance, a dedicated database (published database as shown in Fig.3) is introduced to keep the processed data and handle all consumer requests exclusively. The publishing framework populates published data periodically under a preconfigured schedule. This process is not intended to be ETL (extract, transform and load) for data warehousing to support BI (business intelligence) platform, it can however, architecturally accommodate such requirement as a potential.
In terms of terminal technologies, RFID and 2D barcode are the two commonly adopted options. Both of them can carry much more data than the conventional 1D barcode and both of them have successful implementations in traceability systems. Despite the great potential of RFID, there are still major technical and business barriers preventing its common implementation. On the other hand, 2D barcode is proven to be matured, cost effective and user friendly. In our system, both of RFID and QR code (a type of commonly used 2D barcode) are adopted as alternative.

-
Utility Company Business Growth Model and Decision Support System
Finding power to supply its customers is the first thing a newly established utility company needs to do. Electricity can be purchased either from the network or from an energy producer directly. The... -
A Brief View of Business Intelligence
The Data Warehouse Institute defines Business Intelligence as the processes, technologies and tools needed to turn data into information and information into knowledge and knowledge into plans that dri... -
Whole Life Costing Model in Asset Management
In asset management, the whole life costing model is normally initiated to meet the following two broad strategic objectives: to ensure sufficient funding is available to maintain the asset portfolio... -
Apply Artificial Intelligence in Retail Promotion to Reduce Food Waste
Artificial intelligence (AI) is an academic field that studies how to create computers and computer software which are capable of intelligent behavior. The major concerns of AI research include reason... -
A Conceptual Framework for Reducing Consumer Food Waste
Our framework is based on the concept of a closed-loop control system from control engineering. It employs the Internet of Things (IoT) sensor network to realize a closed-loop consumer food consumptio... -
Diffuse Traceability Across Food Industry
The implementation of traceability in food industry has been required as mandatory in some countries. In Europe for instance, the General Food Law entered into force in 2002 which makes traceability c... -
A Centralized Traceability System for SMEs
Our centralized traceability system (CTS) consists of three function modules: traceability server, database server and web portal. It creates very few overheads for supply chain partners as the server...

-
Identify Potential Customer for Corporate Bank
Our client serves UK businesses ranging from SMEs to International Corporation. Their major products include business loans, asset finance, invoice finance and international services. When a new promo... -
Usage Forecasting for Utility Industry
We assist utility companies in developing a profit optimization model for their business, based on the use of ‘smart-meters’ which enable instantaneous registration of customer usage. To achieve optim... -
Personal Care and Cosmetics Product Stability Testing
The purpose of stability testing for personal care and cosmetics products is to ensure that a new or modified product meets the intended physical, chemical and microbiological quality standards as wel... -
Analytics on Weather and Customer Demand
For big supermarket chains, retail profits depends on meeting customer demands on a large number of Stock Keeping Units (SKU) across hundreds of stores. Weather is a key factor which influences custom... -
Identifying the FactorsDriving the Fault Rate of Network Connection and Resource Allocation Optimization
Providing reliable network connection and services to customers is crucial to telecom companies' success. Faulty connection is very costly for the firms. Thus, great value in the form of cost reductio... -
Business Analytics in Rolling Stock Maintenance Strategy Optimization
The reliable and safe operation of rolling stock requires huge investment in maintenance. To protect the investment and the sustainability of rolling stocks, it is vital to maintain the assets as econ...














